Extroducer publications
- Lundberg, J., Johansson, C. B., Jonsson, S. & Holmin, S. Access to the brain parenchyma using endovascular techniques and a micro-working channel. Journal of Neurosurgery 1–7 (2016).
- Lundberg, J. et al. Endovascular Method for Transplantation of Insulin-Producing Cells to the Pancreas Parenchyma in Swine. American Journal of Transplantation 14, 694–700 (2014).
- Lundberg, J. et al. Liver parenchyma access and lesion marker via the endovascular route. Journal of Surgical Research 195, 488–494 (2015).
- Lundberg, J., Jonsson, S. & Holmin, S. Long Term Follow-Up of the Endovascular Trans-Vessel Wall Technique for Parenchymal Access in Rabbit with Full Clinical Integration. PLoS ONE 6, e23328–6 (2011).
- Lundberg, J., Jonsson, S. & Holmin, S. New Endovascular Method for Transvascular Exit of Arteries and Veins: Developed in Simulator, in Rat and in Rabbit with Full Clinical Integration. PLoS ONE 5, e10449–9 (2010).
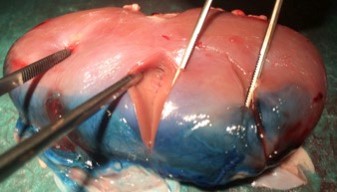
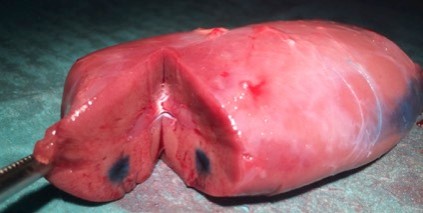
Kidney
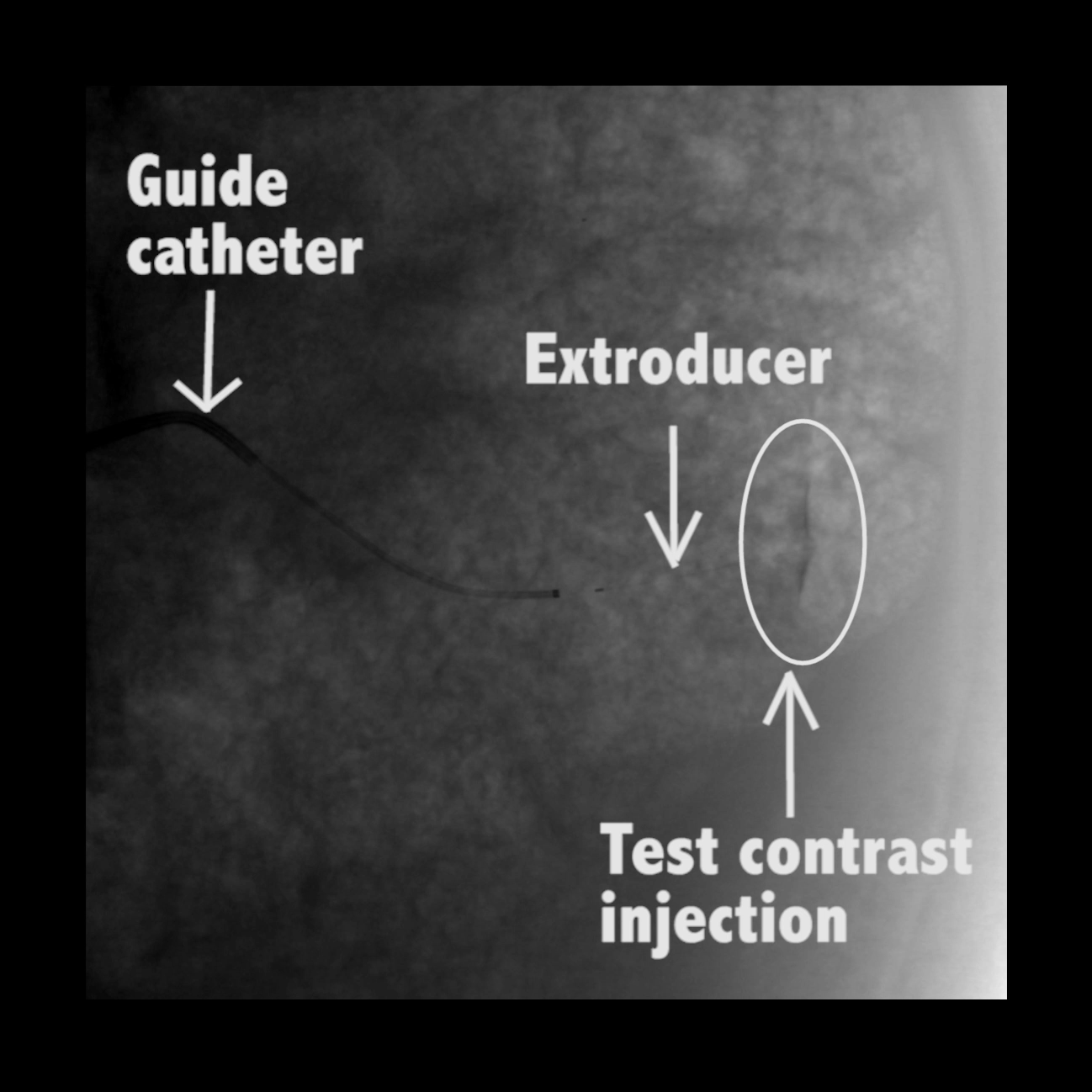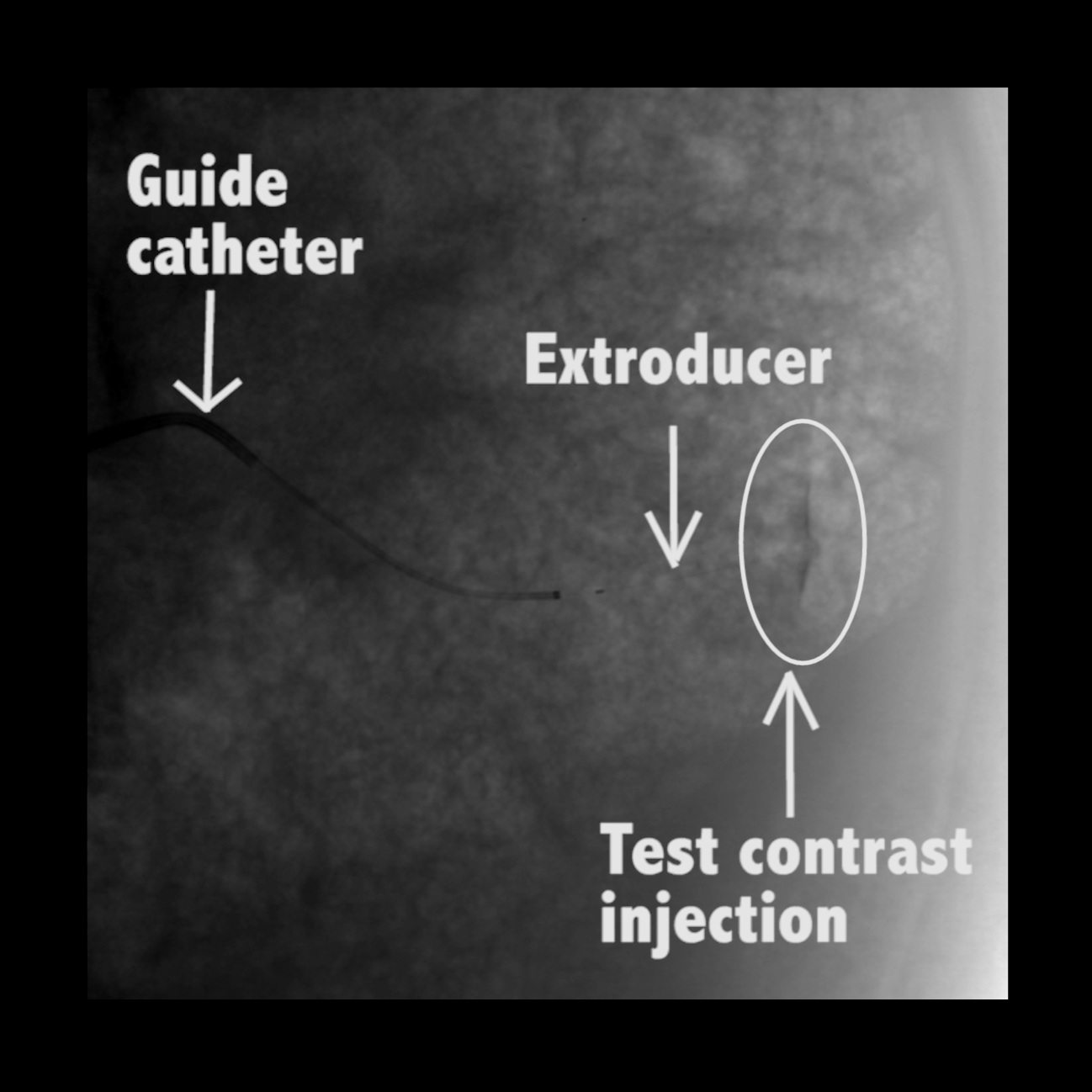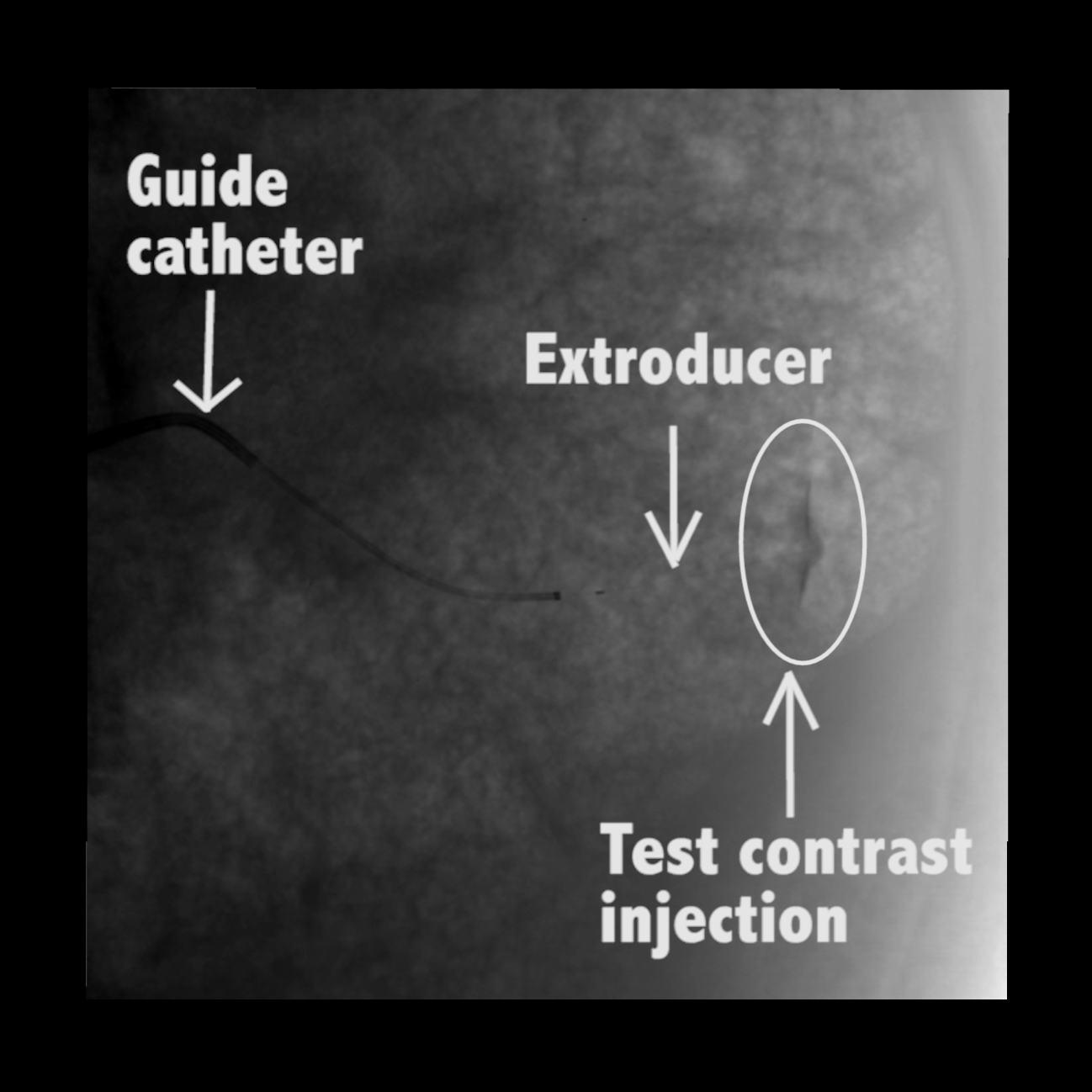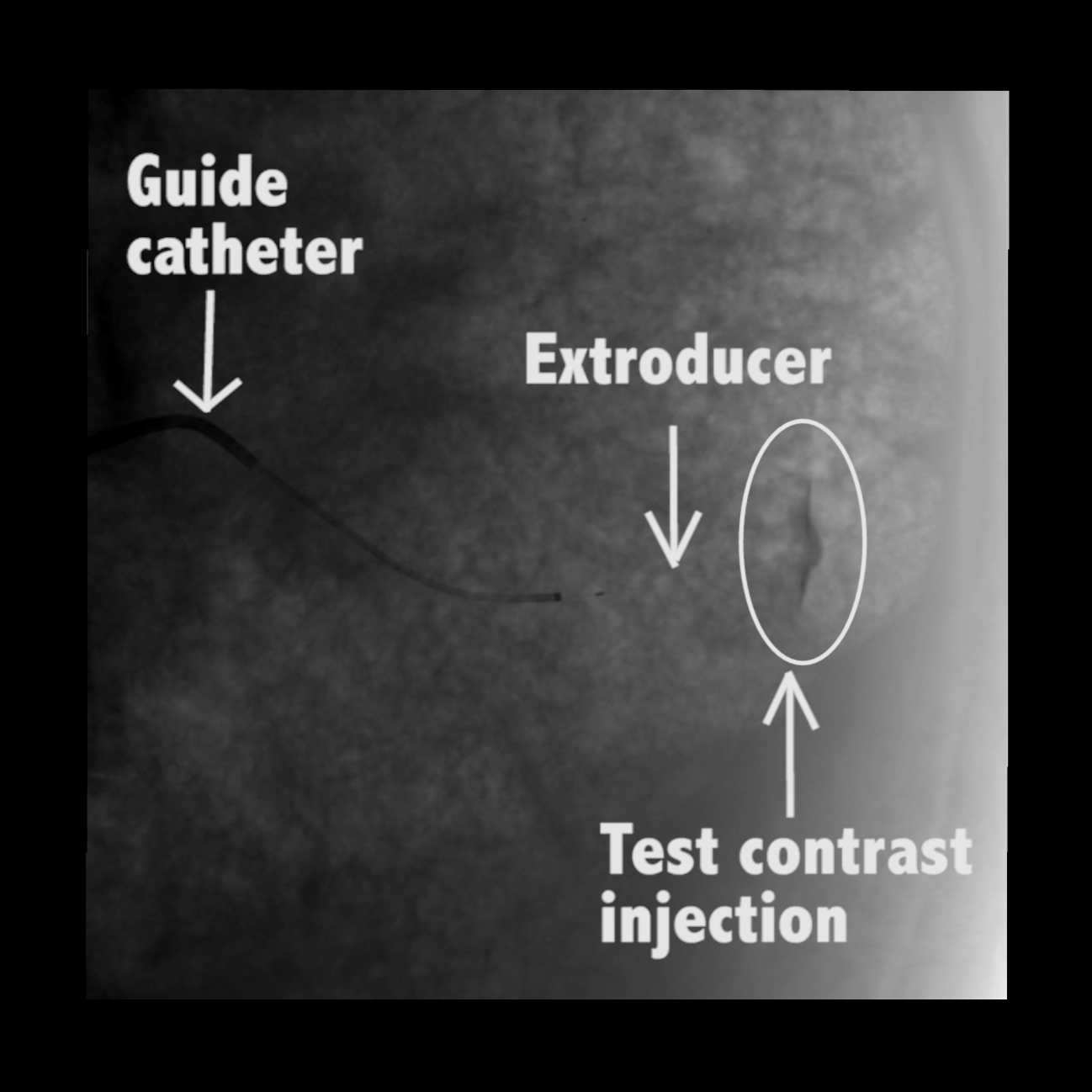
In large animal research studies at the Karolinska Institute, the Extroducer could deliver test payloads to the kidney tissue and kidney capsule.
-
Unique ability to inject into the kidney capsule, “painting” the kidney surface
-
Injections directly into the kidney
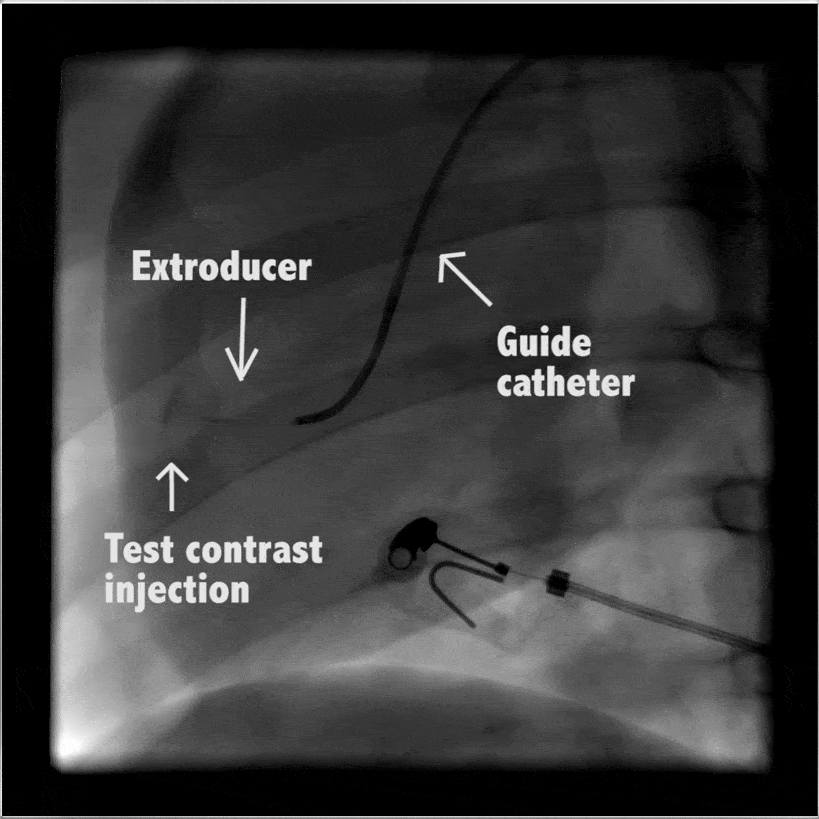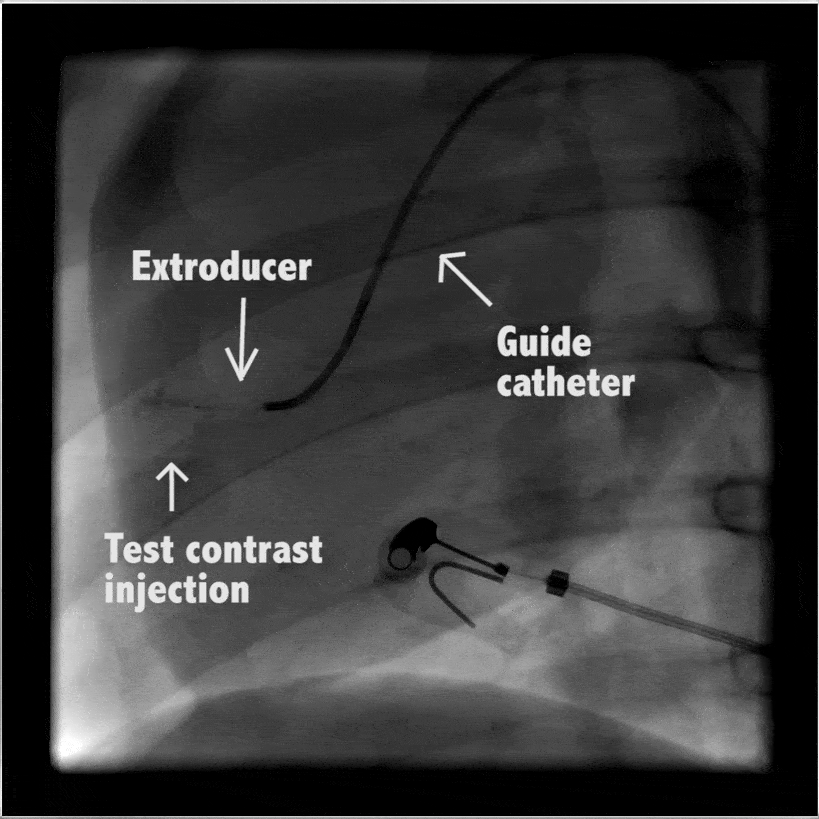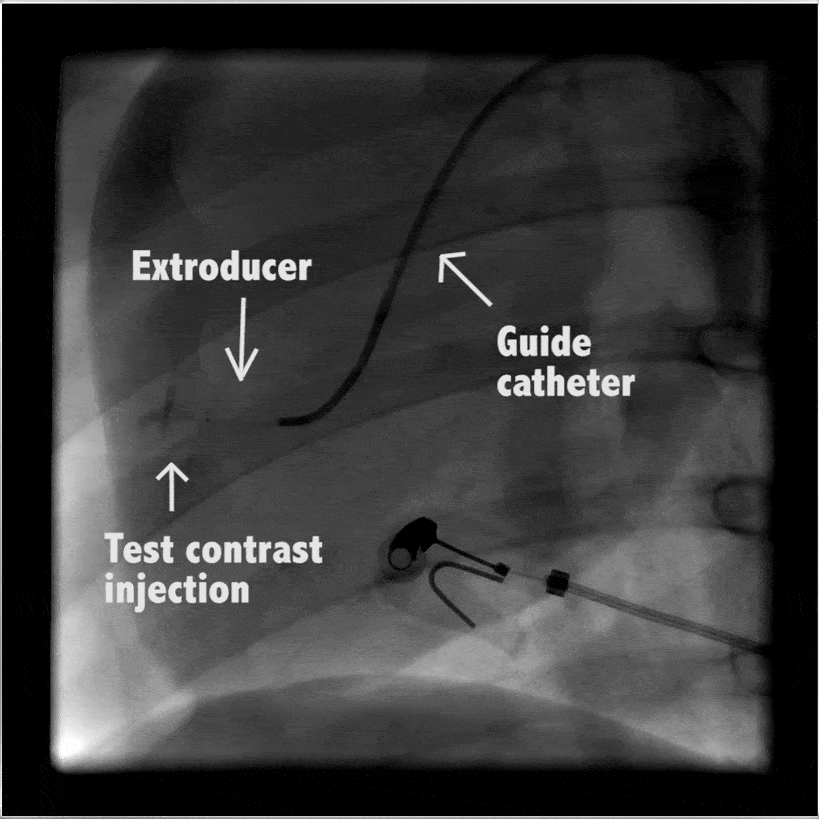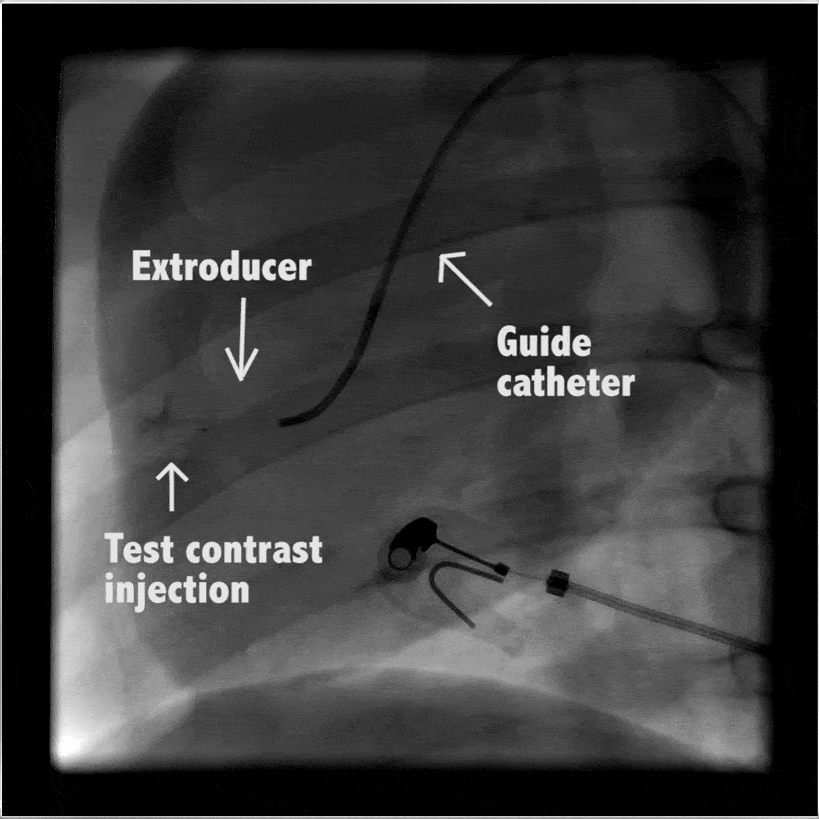
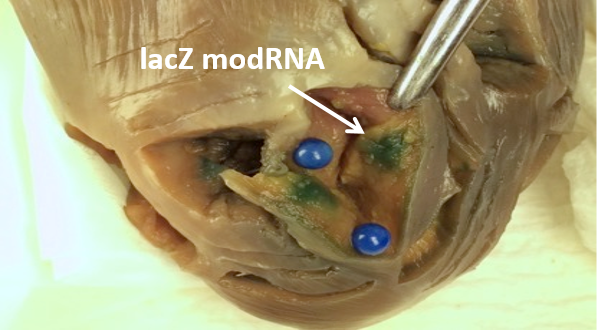
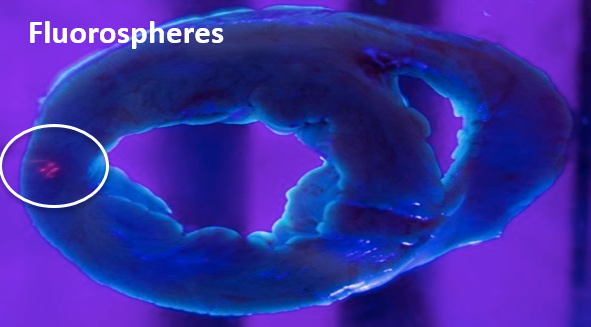
Heart
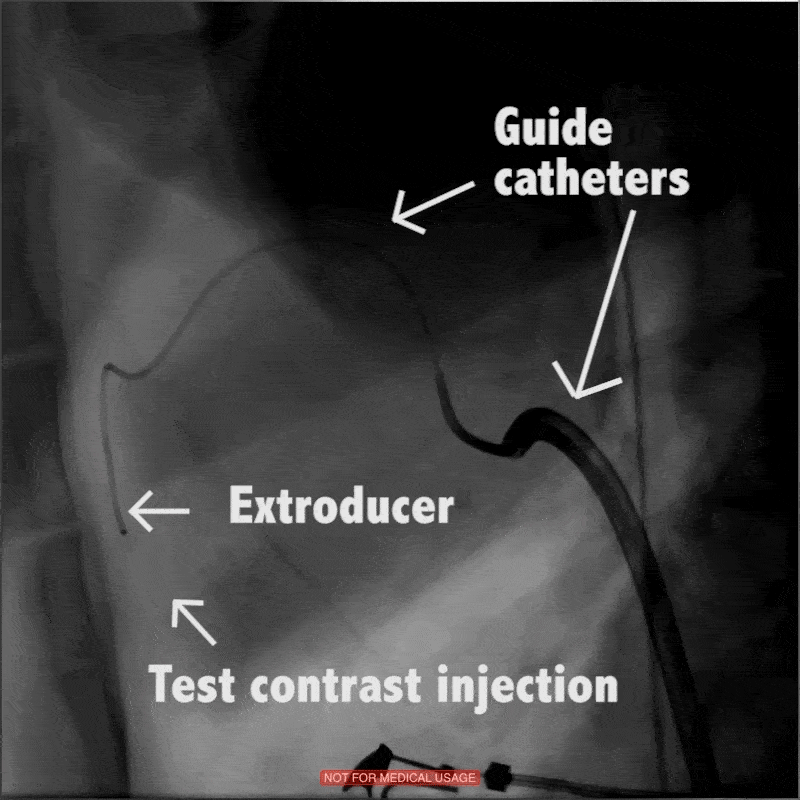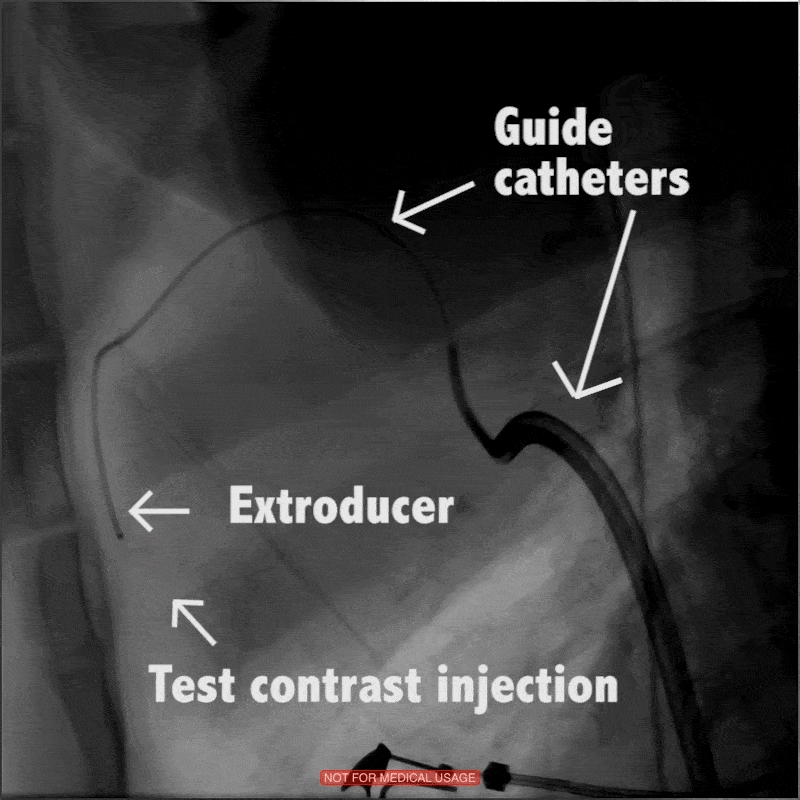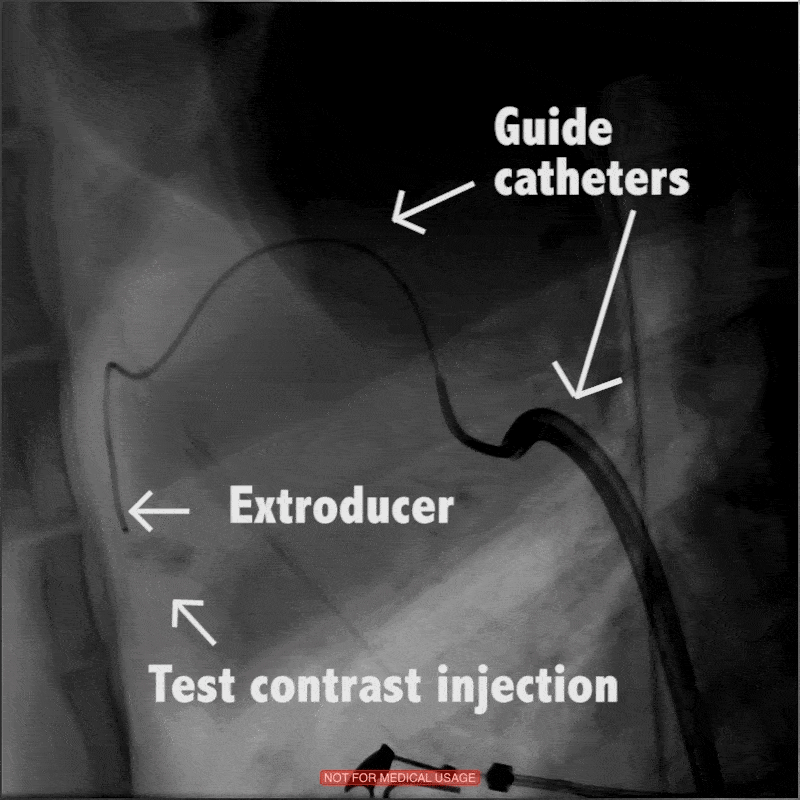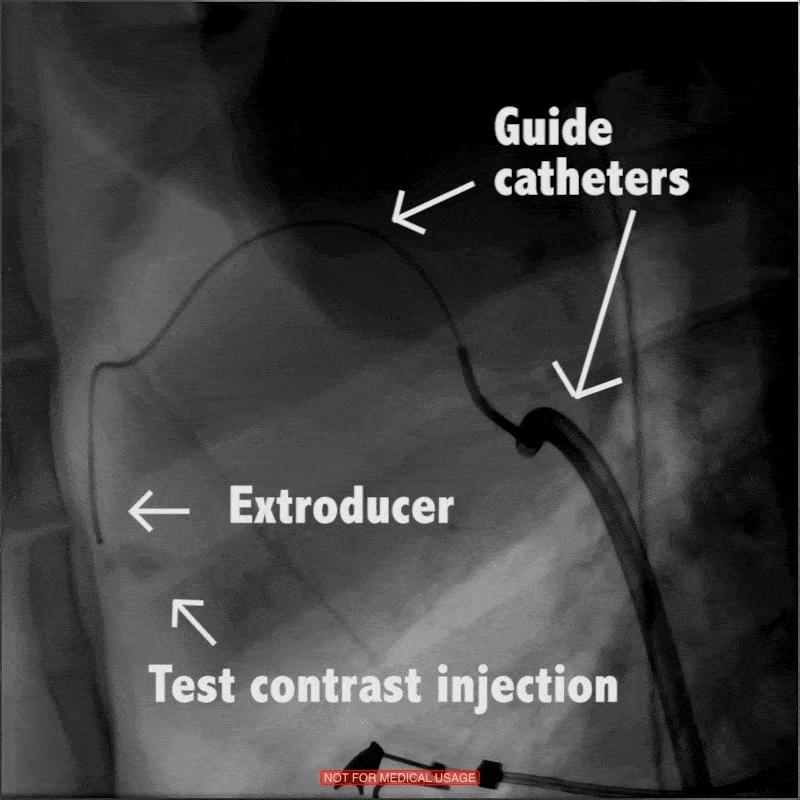
In large animal research studies at the Karolinska Institute, the Extroducer can delivery test payloads to the heart, both from the inside and the surface, accessing different layers of the heart muscle.
-
Injection of modified RNA from outer surface epicardial vein
-
Injection of fluorospheres from inside the heart